The food technology sector is undergoing a revolutionary transformation as scientists and startups pioneer methods to create authentic-tasting plant-based meats through cellular agriculture. Among the most challenging and promising developments is the cultivation of muscle fibers that replicate the texture and mouthfeel of traditional steak – without animal slaughter.
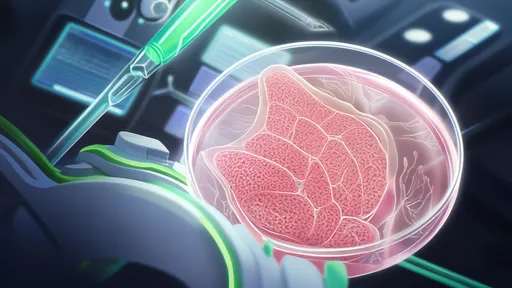
From petri dish to dinner plate, researchers are leveraging advances in tissue engineering to grow bovine muscle cells in controlled environments. Unlike ground beef alternatives that dominate today's market, these next-generation products aim to recreate the complex grain and chew of premium cuts. The process begins with isolating stem cells from cattle through harmless biopsies, which are then multiplied in nutrient-rich bioreactors.
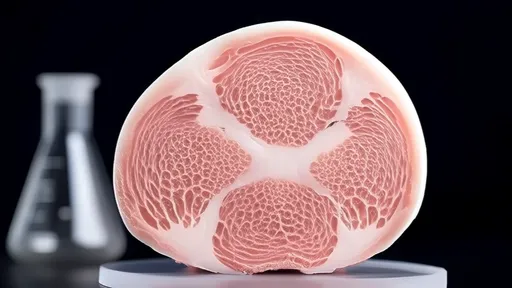
What makes steak distinctive lies in its fibrous architecture. Muscle cells naturally align into parallel bundles during animal growth, creating the characteristic grain that gives steak its texture. Reproducing this structure without the animal requires innovative scaffolding techniques. Some companies use 3D-printed edible frameworks made from plant proteins, while others employ magnetic or electrical stimulation to encourage proper fiber alignment.
The nutrient medium poses another critical challenge. Traditional cell culture relies on fetal bovine serum, which defeats the purpose of animal-free meat. Cutting-edge solutions now utilize plant-derived growth factors and precision fermentation to create completely vegan nutrient cocktails. These advances have reduced production costs dramatically since the first $300,000 lab-grown burger in 2013.
Temperature and mechanical stress play crucial roles in developing meat-like textures. Just as livestock muscles develop through movement, bioengineered muscle fibers require periodic stretching and compression to achieve optimal density. Specialized bioreactors now simulate these natural conditions through precisely controlled environmental parameters.
The flavor frontier presents its own complexities. While muscle fibers provide texture, the distinctive taste of beef comes from fat distribution and heme proteins. Companies are addressing this by co-culturing adipocytes (fat cells) with muscle cells and using plant-based heme alternatives. The result is marbling that melts during cooking, releasing authentic beefy flavors.
Scaling production remains the industry's greatest hurdle. Laboratory methods that work for small batches often fail when translated to industrial scales. Engineers are designing next-generation bioreactors that can maintain perfect conditions for thousands of liters of culture simultaneously while preventing contamination – a persistent issue in large-scale cell culture operations.
Regulatory pathways are evolving alongside the technology. Several countries have established frameworks for cultured meat approval, with Singapore leading as the first to grant regulatory clearance. The U.S. FDA and USDA have developed a joint regulatory approach, focusing on cell line safety and production controls.
Consumer acceptance studies reveal generational divides. While younger demographics show strong interest in these sustainable alternatives, traditional meat eaters often express skepticism about "lab-grown" products. Marketing strategies increasingly emphasize the technology's benefits – reduced land use, lower greenhouse emissions, and elimination of slaughter – rather than the laboratory origins.
The environmental calculus appears favorable. Life cycle assessments suggest cultured meat could reduce land use by more than 95% and greenhouse gas emissions by 80-90% compared to conventional beef production. Water savings are equally dramatic, with estimates ranging from 78-96% reduction depending on production methods. These figures assume renewable energy powers the facilities – an essential factor in achieving sustainability goals.
Economic models predict price parity with premium beef within this decade. Current production costs hover around $50 per pound for high-quality cultured steak, down from thousands just years ago. The trajectory suggests mainstream affordability as processes optimize and scale increases. Industry analysts project the global cultured meat market could reach $25 billion by 2030.
Nutritional customization offers another advantage over conventional meat. Producers can adjust fat profiles to increase healthy omega-3s or reduce saturated fats. Iron and vitamin content can be enhanced through media formulation, creating functionally optimized meat products. Some prototypes already demonstrate superior nutritional profiles to their animal-derived counterparts.
The supply chain implications are profound. Traditional livestock farming requires vast amounts of feed crops, whereas cellular agriculture uses nutrients directly. This efficiency could fundamentally alter agricultural land use patterns, potentially returning millions of acres to natural habitats. The geographical distribution of meat production may shift as well, with facilities located near population centers rather than feed sources.
Technical hurdles persist in achieving truly steak-like products. The extracellular matrix that gives meat its structural integrity remains difficult to replicate perfectly. Some companies are exploring plant-derived collagen alternatives, while others use innovative texturization techniques involving temperature cycling and enzymatic treatments.
Intellectual property landscapes are becoming increasingly complex as companies race to patent key processes. Over 1,000 patents related to cultured meat have been filed globally, covering everything from specialized bioreactor designs to serum-free media formulations. This rapid innovation is driving down costs while raising important questions about technology access and equitable development.
As the technology matures, hybrid products combining plant proteins with cultured cells may bridge the gap during market transition. These blends could offer more affordable entry points while still providing substantial environmental benefits compared to conventional meat. Several companies already market products containing 10-50% cultured meat mixed with plant-based ingredients.
The culinary world watches these developments closely. Top chefs experiment with prototypes, noting that cultured meats cook differently than their conventional counterparts due to variations in fat distribution and connective tissue. This requires new cooking techniques and recipe development – an exciting frontier for innovative cuisine.
Ethical considerations extend beyond animal welfare. While eliminating slaughter addresses one moral concern, questions remain about the long-term impacts on farming communities and food sovereignty. Some advocate for inclusive transition strategies that support agricultural workers through this technological shift.
Looking ahead, the next five years will likely determine whether cultured steak can move from boutique production to supermarket shelves. As production scales and prices drop, the combination of environmental benefits and culinary quality may prove irresistible to consumers and policymakers alike. The sizzle of the future might just come from a bioreactor rather than a pasture.

By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025
By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025
By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025
By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025

By /Jul 11, 2025